

progress: shows the percentage of the copying process and the remaining time. exclude: certain files or folders will be ignored when copying. delete: rsync will delete the files in the destination folder that are not present in the source folder. a: it shows the original information of the file, such as timestamp, permissions, owner etc. h: instead of showing the size of the copied files in bytes, an easily readable format will be shown ( rather than 14.167.396 bytes, 14.17 Mb will be seen) r: to copy the folders and their contents v: the copied files and folders will be shown on the shell Syntax $ rsync options /path/source/ /path/destination/
UBUNTU GRSYNC INSTALL
To install it type: $ sudo apt install rsync The rsync packages are already present in the Official Ubuntu Repository.
UBUNTU GRSYNC HOW TO
In this article you will learn how to install, configure and use Rsync on Linux Ubuntu 18.04 in order to synchronize files and folders and schedule a periodic backup of your server. What distinguishes Rsync from the classic “copy and paste” is that this tool automatically recognizes which documents differ between two folders, so as to speed up the copying process from a source folder to a destination. The new versions of rsync are configured to use SSH as default remote shell.Rsync (Remote sync) is a tool to copy and synchronize files and folders on the same server or between different machines on Linux. , it must be installed on both the source and the destination machine. When using rsync to transfer data remotely Using rsync to Sync Data from/to a remote Machine # When the trailing slash is omitted, rsync copies the source directory inside the destination directory. If the source directory has a trailing slash, the command will copy only the directory contents to the destination directory. It is worth mentioning that rsync gives different treatment to the source directories with a trailing slash ( /). The example below shows how to create a local backup of website files: rsync -a /var/If the destination directory doesn’t exist, rsync will create it. The real power of rsync comes when synchronizing directories. If you want to save the file under a different name, specify the new name on the destination part: rsync -a /opt/filename.zip /tmp/newfilename.zip Omitting the filename from the destination location copies the file with the current name. The user running the command must have read permissions on the source location and write permissions on the destination.
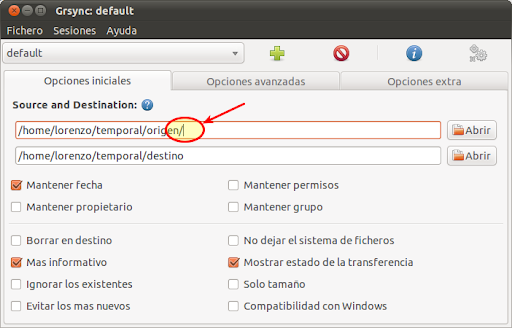
Here is an example: rsync -a /opt/filename.zip /tmp/ The most basic use case of rsync is to copy a single file from one to another local location. By default, rsync is configured to use ssh. This option allows you to choose a different remote shell. Use this option if you want to suppress non-error messages. When this option is used, rsync deletes extraneous files from the destination location. It is useful when transferring large files over slow or unstable network connections. When this option is used, rsync shows a progress bar during the transfer and keeps the partially transferred files. Use this option only if the connection to the remote machine is slow. This option forces rsync to compresses the data as it is sent to the destination machine. This option tells rsync to syncs directories recursively, transfer special and block devices, preserve symbolic links, modification times, groups, ownership, and permissions.
UBUNTU GRSYNC ARCHIVE
-a, -archive, archive mode, equivalent to -rlptgoD.Rsync provides a number of options that control how the command behaves. The rsync utility expressions take the following form: Install Rsync on Ubuntu and Debian # sudo apt install rsync Install Rsync on CentOS and Fedora # sudo yum install rsync Rsync Command Syntax #īefore going into how to use the rsync command, let’s start by reviewing the basic syntax. If you don’t have rsync installed on your system, you can easily install it using your distribution’s package manager. The rsync utility is pre-installed on most Linux distributions and macOS. This article explains how to use rsync through practical examples and detailed explanations of the most common rsync options. Rsync can be used for mirroring data, incremental backups, copying files between systems, and as a replacement for scp It provides fast incremental file transfer by transferring only the differences between the source and the destination. Rsync is a fast and versatile command-line utility for synchronizing files and directories between two locations over a remote shell, or from/to a remote Rsync daemon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
